Question 1: [1 mark]
Choose the correct definition for the turning point of a quadratic graph.
Answer type: Multiple choice type 1
A: The turning point of a quadratic graph is where the gradient is equal to 0.
B: The turning point of a quadratic graph is where the graph crosses the x axis.
C: The turning point of a quadratic graph is always the minimum point.
D: The turning point of a quadratic graph is always (0,0).
ANSWER: A: The turning point of a quadratic graph is where the gradient is equal to 0.
Question 2: [2 marks]
Choose the correct turning points for the following graph.
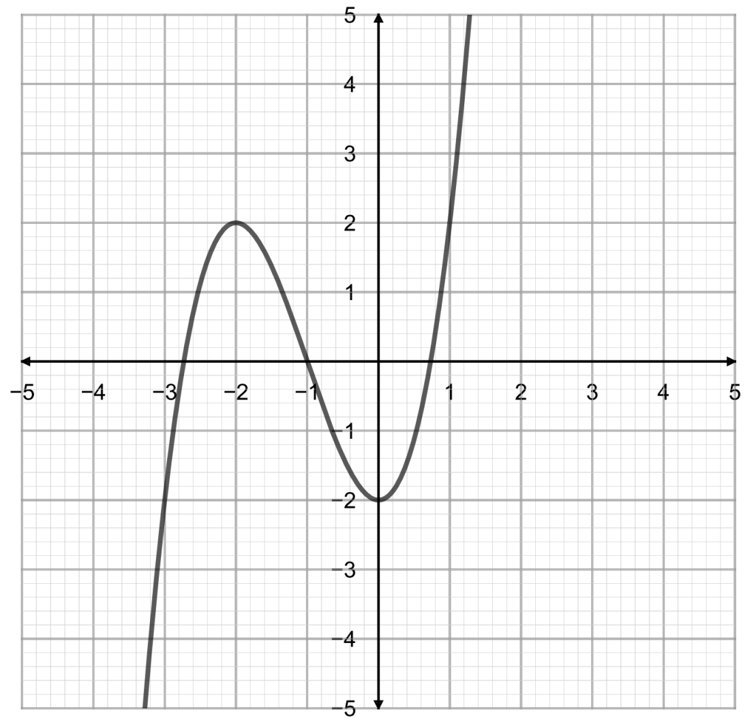
Answer type: Multiple choice type 1
A: (-2,2) and (0,-2)
B: (2,-2) and (0,-2)
C: (-2,2) and (-2,0)
D: (2,-2) and (-2,0)
ANSWER: A: (-2,2) and (0,-2)
WORKING:
The turning points of a quadratic graph is where the gradient is equal to 0.
Question 3: [2 marks]
Choose the correct turning points for the following graphs.
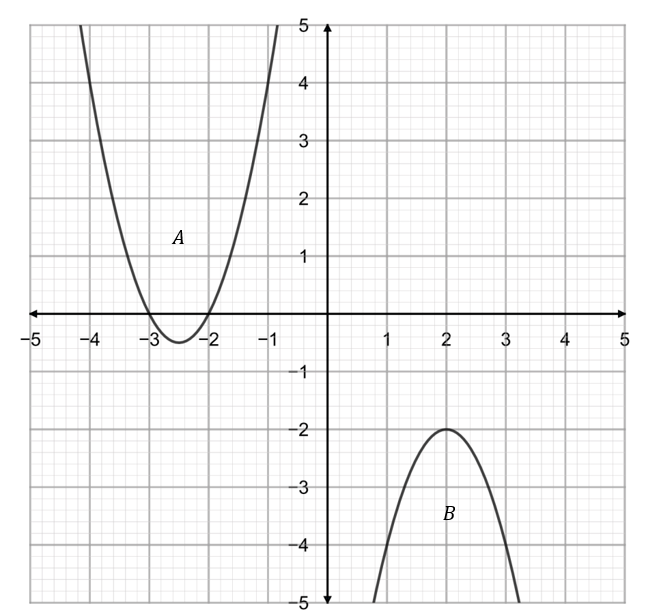
Answer type: Multiple choice type 1
A: A: \, (-2.5, -0.5) and B: \, (2,-2)
B: A: \, (-0.5, -2.5) and B: \, (-2,2)
C: A: \, (2, -2) and B: \, (-2.5, -0.5)
D: A: \, (-2, 2) and B: \, (-0.5, -2.5)
ANSWER: A: A: \, (-2.5, -0.5) and B: \, (2,-2)
WORKING:
The turning points of quadratic graphs is where the gradient is equal to 0.
Question 4:
Find the turning point of the following equations by completing the square.
Question 4(a): [2 marks]
y = x^2 + 4x + 7
Answer type: Multiple choice type 1
A: (-2,3)
B: (2,3)
C: (3, -2)
D: (3,2)
ANSWER: A: (-2,3)
WORKING:
y = (x+2)^2 + 3
x = -2, \, y = 3
Question 4(b): [2 marks]
y = 3x^2 + 36x + 99
Answer type: Multiple choice type 1
A: (-6,-9)
B: (6,- 9)
C: (6,-3)
D: (-6,-3)
ANSWER: A: (-6,-9)
WORKING:
y = 3(x^2 + 12x + 33)
= 3[(x+6)^2 - 3] = 3(x+6)^2 - 9
x = -6, \, y = -9
Question 4(c): [2 marks]
y = 2x^2 + 7x - 10
Answer type: Multiple choice type 1
A: \bigg( - \dfrac{7}{4}, - \dfrac{129}{8} \bigg)
B: \bigg( \dfrac{7}{4}, \dfrac{129}{8} \bigg)
C: \bigg( - \dfrac{129}{8}, - \dfrac{7}{4} \bigg)
D: \bigg( \dfrac{129}{8}, \dfrac{7}{4} \bigg)
ANSWER: A: \bigg( - \dfrac{7}{4}, - \dfrac{129}{8} \bigg)
WORKING:
y = 2 \bigg(x^2 + \dfrac{7}{2} - 5 \bigg)
= 2 \bigg[ \bigg(x + \dfrac{7}{4} \bigg) ^2 - \dfrac{129}{16} \bigg]
= 2 \bigg(x + \dfrac{7}{4} \bigg) ^2 - \dfrac{129}{8}
x = -\dfrac{7}{4}, \, y = - \dfrac{129}{8}
Question 5:
Choose the correct turning points for the following graphs.
Question 5(a): [1 mark]
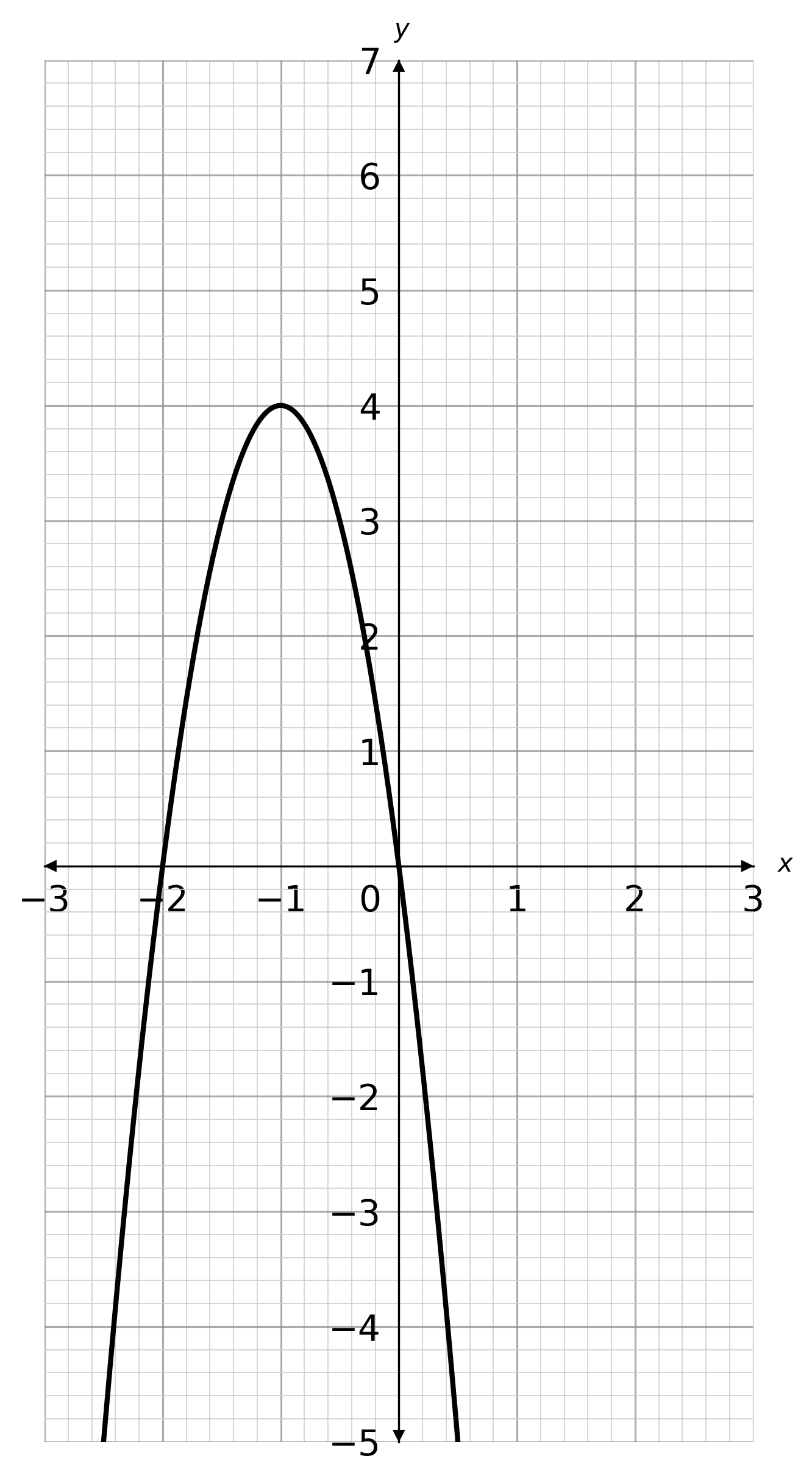
Answer type: Multiple choice type 1
A: (-1,4)
B: (0,0)
C: (-2,0)
D: (4,-1)
ANSWER: A: (-1,4)
WORKING:
The turning point of a quadratic graph is where the gradient is equal to 0
Question 5(b): [1 mark]
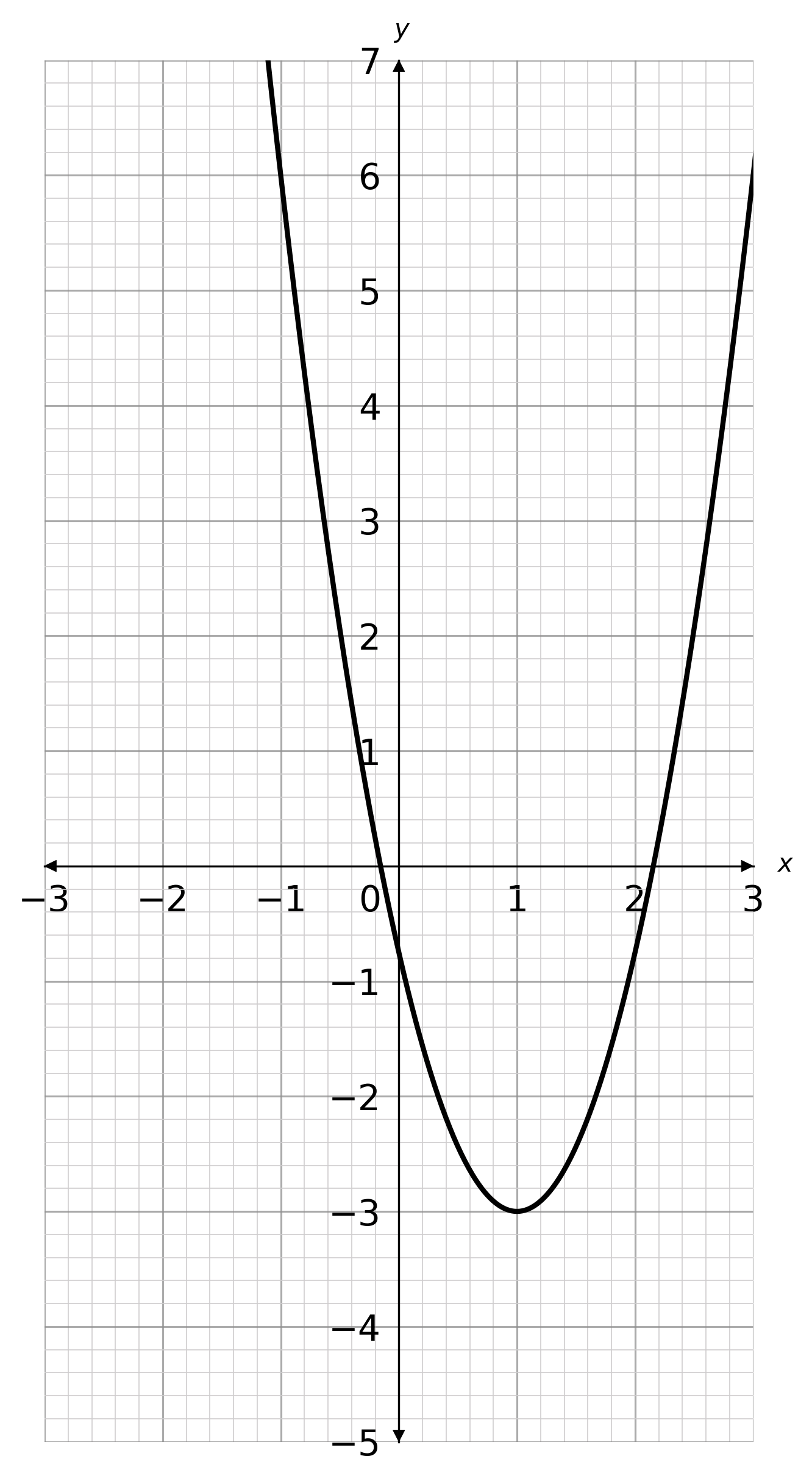
Answer type: Multiple choice type 1
A: (1,-3)
B: (0,-0.75)
C: (-3,1)
D: (0, 0.75)
ANSWER: A: (1,-3)
WORKING:
The turning point of a quadratic graph is where the gradient is equal to 0
Question 6:
Find the turning point of the following equations by completing the square.
Question 6(a): [2 marks]
y = x^2 + 16x + 49
Answer type: Multiple choice type 1
A: (-8,-15)
B: (8,-15)
C: (8,113)
D: (-8,113)
ANSWER: A: (-8,-15)
WORKING:
y = (x+8)^2 - 15
x = -8, \, y = -15
Question 6(b): [2 marks]
y = 2x^2 + 12x - 4
Answer type: Multiple choice type 1
A: (-3,-22)
B: (3, -22)
C: (-3,-11)
D: (-3,-4)
ANSWER: A: (-3,-22)
WORKING:
y = 2(x^2 + 6x - 2)
= 2[(x+3)^2 - 11]
= 2(x+3)^2 - 22
x = -3, \, y = -22
Question 6(c): [2 marks]
y = 5x^2 + 18x - 7
Answer type: Multiple choice type 1
A: \bigg( - \dfrac{9}{5}, - \dfrac{116}{5} \bigg)
B: \bigg( \dfrac{9}{5}, - \dfrac{116}{5} \bigg)
C: \bigg( - \dfrac{9}{5}, - \dfrac{116}{25} \bigg)
D: \bigg( - \dfrac{9}{5}, - \dfrac{46}{5} \bigg)
ANSWER: A: \bigg( - \dfrac{9}{5}, - \dfrac{116}{5} \bigg)
WORKING:
y = 5 \bigg( x^2 + \dfrac{18}{5}x - \dfrac{7}{5} \bigg)
= 5 \bigg[ \bigg(x+\dfrac{9}{5} \bigg)^2 - \dfrac{116}{25} \bigg]
= 5 \bigg(x + \dfrac{9}{5} \bigg)^2 - \dfrac{116}{5}
x = - \dfrac{9}{5} , \, y = - \dfrac{116}{5}
